RENDERINGS
AS BUILT/CONSTRUCTION
DETAILS
KPM provided Structures and MEP design services for this 140,000 sqm Mall is designed to meet LEED Gold standards. The Park is located within Hyderabad city next to a metro station and will include 3 basements plus 6 levels of retail with higher-than-standard floor- to-floor heights and a community park at level3. The cost of Operation is reduced by use of high COP chillers, efficient use of heat recovery systems and on-site generation of solar power.
■ Structural solutions were designed for flexibility and provided the opportunity for the complete change to the floor layouts and use at each level in the future.
■ The MEP design included provision of a standalone sewage and wastewater treatment plant for the development. Treated water from the plant was used for irrigation.
■ Photovoltaics were also provided to generate 5% of the power consumption of the building to further enhance the developments sustainability credentials.
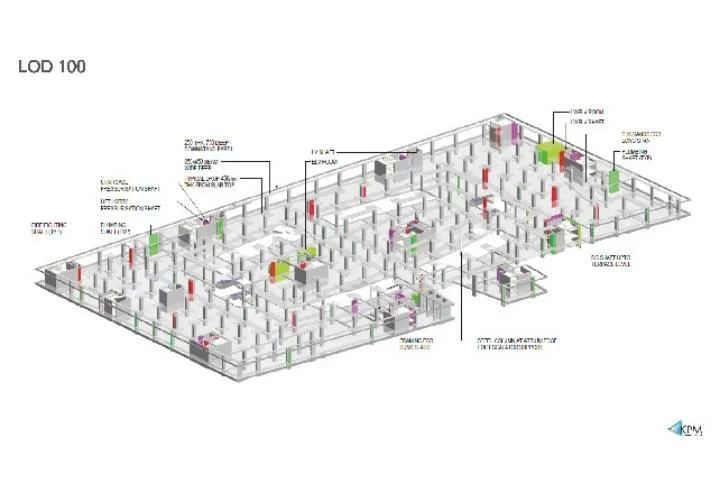
CHALLENGES
Structures: The mall has 3 Basements and 5 floors with different occupancies such as a landscape area, retail space, a park on 3rd floor, and multiple theaters at the top level. The higher water table levels were observed on-site during the geotechnical investigation. MEP: The project was the development of a mall building. As the floor to floor to heights were 4.5 m the client wanted to understand the maximum false ceiling heights available in the corridor during the concept stage.
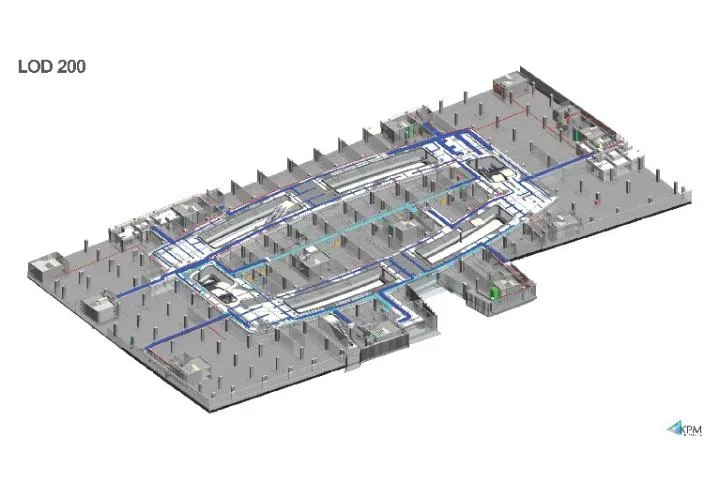
SOLUTIONS
Structures: The mall had 13 major cores out of which 3 cores had the maximum number of MEP services running horizontally which would determine the false ceiling heights when these services entered the public areas. Based on the architectural Revit model a fully coordinated structural and MEP was modeled at these three cores. Based on the modeled services the achievable false ceiling heights were conveyed to the client.
MEP: Each floor has different architectural intent with different floor-to-floor heights. The global and local structural systems were adopted to stabilize the structure along with the transfer systems to fulfill the architectural requirements. Subsoil drainage under the raft and footing was provided to control the water pressure acting on it.















